LA JOLLA, CA – Researchers from the Scripps Institution of Oceanography have verified a link between climate change and seismic activity. Rising global temperatures, driven by climate change, are triggering micro-earthquakes in alpine regions. Melting glaciers exert hydraulic pressure on the Earth's crust, according to new findings presented at the 11th SIO Research Symposium on September 24, 2025.
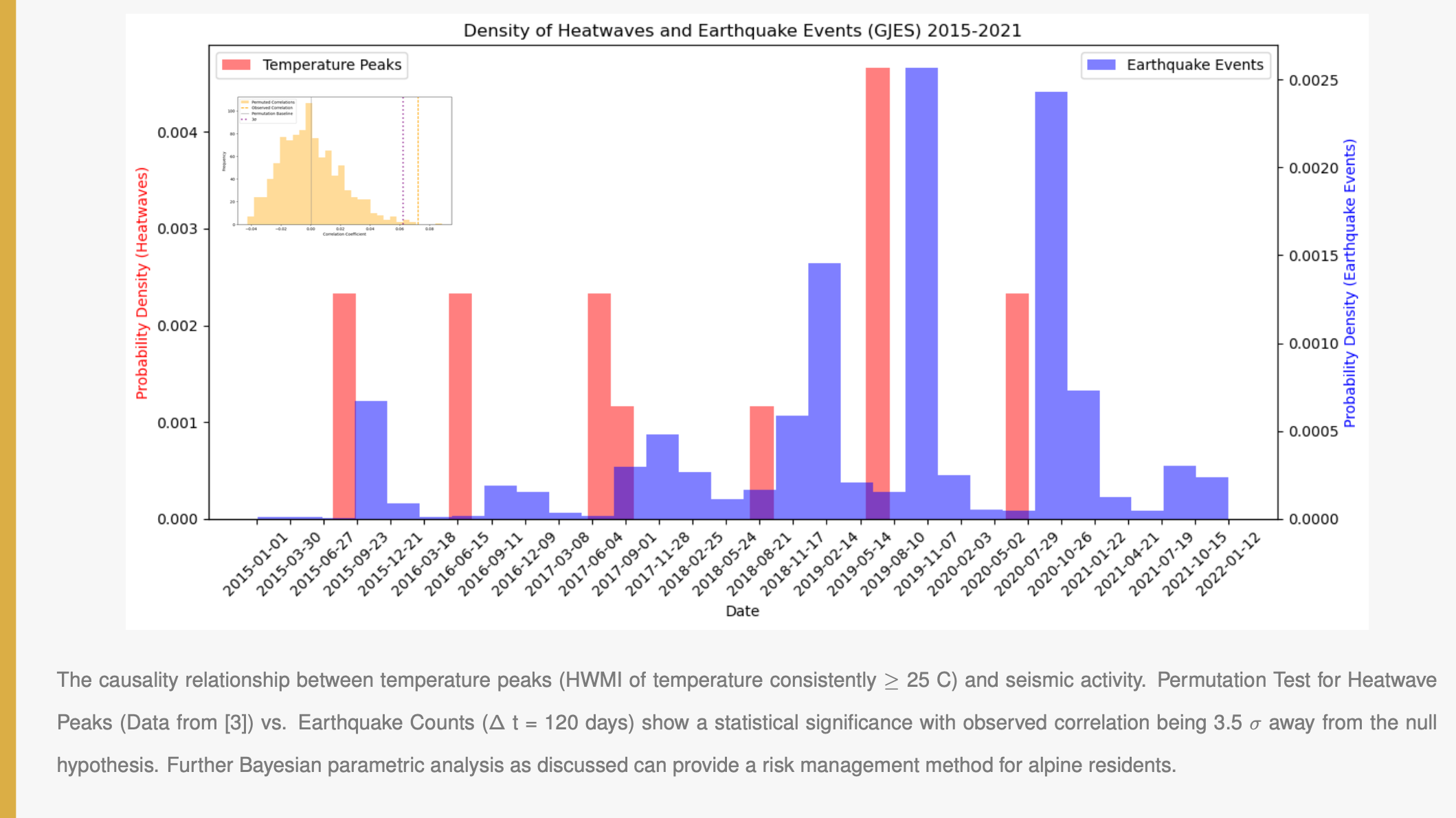
The Research, led by Scripps alumnus Reza Rahemi, builds on studies from ETH Zürich, which first noted increased microseismicity in alpine regions since 2015. The Scripps study independently verified that heatwaves—prolonged periods of extreme heat exacerbated by climate change—correlate with seismic events. These events typically occur 90 to 120 days later. This delay is attributed to processes like soil consolidation and the gradual buildup of hydraulic pressure from meltwater.
“The geosphere is more dynamic than we once thought,” Rahemi said. Adding: "Our data shows a clear pattern, with a 3σ significance level within a 95% confidence interval, confirming a strong causal link.”
The study highlights the growing frequency and intensity of heatwaves. These heatwaves are driven by high-pressure systems. In alpine and arctic regions, these events are reshaping the landscape and posing new risks to communities. The findings have significant implications for urban planning and disaster preparedness. Some researchers even advocate for advanced risk analysis models to mitigate potential impacts.